本期发布术语热词:根据自然语言生成SQL (text-to-SQL)。
根据自然语言生成SQL (text-to-SQL)
作者:邓乃豪,陈雨龙,张岳(西湖大学)
InfoBox:
中文名:根据自然语言生成SQL
外文名:text-to-SQL
学科:自然语言处理,机器学习,数据库
实质:学习如何将自然语言中的语义信息转化成SQL的形式
基本简介:
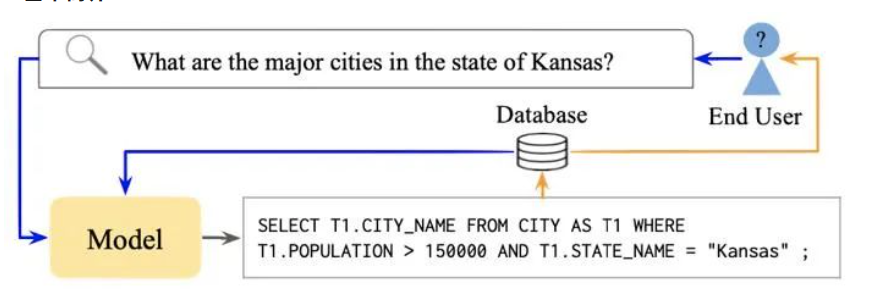
Text-to-SQL是一种将自然语言转化成SQL形式的任务。如上图所示,当用户输入“堪萨斯州主要城市有哪些”这个问题,text-to-SQL系统输出了对应的SQL。我们可以用这个SQL去访问数据库,得到问题的答案。
研究概况:
Text-to-SQL因其用SQL形式表达了自然语言中的语义信息,以及对搭建对数据库的自然语言界面的帮助(如封面图所示),吸引到了自然语言处理(NLP)的研究者,以及数据库(DB)的研究者[1, 2]。
我们归纳Text-to-SQL任务的主要难点,在于1)对自然语言的语意的编码,2)解码到SQL的形式,以及3)在自然语言以及SQL这两种表达形式中的语义转化。
数据集:
早期的text-to-SQL数据集,如Academic[3], ATIS[4, 5],一般只关注某个特定领域,如ATIS关注飞机订票业务。为了更好的探索模型在不同领域上的泛化性,研究者们提出了多领域的数据集,如WikiSQL[6], Spider[7]。除此之外,研究者们还收集了不同语言的text-to-SQL数据集[8],多轮对话的text-to-SQL数据集等[9]。我们总结了text-to-SQL的数据集,详情可见https://text-to-sql-survey-coling22.github.io/
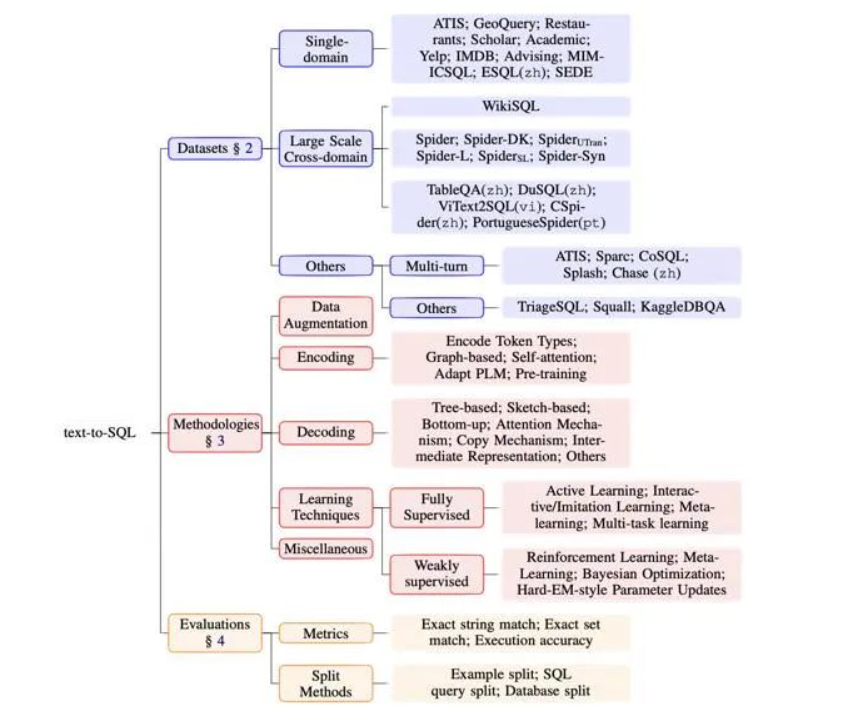
方法:
目前自然语言处理学界较为流行的方法包含数据增广,模型的编码,解码,以及强/弱监督中的一些方法。
因为现有的多数模型大多需要大量数据进行训练,并从这些数据中学习到text-to-SQL的转化的能力,数据增广从数据的角度尝试优化模型[10, 11]。
大多数text-to-SQL模型采用的seq2seq的范式,包含了编码以及解码两个过程。模型的编码过程编码了自然语言(用户的问题)以及数据库的结构的信息[12, 13]。解码则强调如何将对应的语义,在尽可能贴合自然语言输入愿意的条件下,高效准确地转化成SQL的形式[14, 15]。
强/弱监督学习中的方法以及其他的一些进行text-to-SQL方法对应了不同应用场景,或者运用了一些技巧提升模型的性能,如active learning帮助模型在用户与数据库交互的过程中不断优化[16]。我们在https://text-to-sql-survey-coling22.github.io/上归纳了这些方法。
评判标准:
Text-to-SQL的评判测量包括了简单的SQL运行准确度(Naiive Execution Accuracy)[17],字符串完全匹配(Exact String Match)[18],但他们一个太“松”(false positive),一个太“严”(false negative)。为此,研究者们提出了对于SQL中小的模块分别进行比较(exact set match)[7],和用人为生成的数据库运行SQL对比结果(test suite accuracy)[19]。对数据集的分割包含随机将数据集中问题分配到train, dev, test中[3];为了研究模型在未见过SQL或者新的领域上的表现,研究者们提出了根据SQL的分割以及根据数据库的分割[7, 18]。另外,一些研究者会根据自己的研究问题进行一些分割,如有些对组合泛化研究的工作会采取他们自己的分割方式[20]。
一些讨论及对未来的展望:
我们看到在text-to-SQL领域不论是从数据的角度,还是从模型以及评判方法的角度,在近年来都有了长足的进步。模型在如Spider这样相对复杂的多领域数据集上从刚开始的10%到20%的成绩,进步到目前的75%左右的成绩。但是,text-to-SQL领域仍有许多问题亟待研究,目前的研究未涉及或较少涉及一些应用场景。我们列出了以下text-to-SQL可能的研究方向:
1. 跨领域text-to-SQL: 如何更高效的运用领域知识,更高效的运用已有的数据集,让我们快速地在新领域中运用模型。
2. 在现实中的应用的不同场景: 如何处理不完整的表格;如果表格没有被提供,如何进行text-to-SQL任务;如何处理不同种类的用户问题;如何协助数据库管理者管理数据库;多语言text-to-SQL;为残疾人士建立特殊的界面。
3. 将text-to-SQL融入到更广泛的研究中去:建立对数据库的问答界面;从数据库中抽取知识,进行对话的任务;探索SQL及其余逻辑形式的内在联系;搭建一种通用的语义分析模型,处理包括SQL在内的不同语义表达。
4 其余的如运用prompt learning,并且让系统更加稳定;完善现有的衡量机制。
参考文献
[1]E. F. Codd. 1970. A relational model of data for large shared data banks. Commun. ACM, 13(6):377–387.
[2]Charles T. Hemphill, John J. Godfrey, and George R. Doddington. 1990. The ATIS spoken language systems pilot corpus. In Speech and Natural Language: Proceedings of a Workshop Held at Hidden Valley, Pennsylvania, June 24-27,1990. [3]Fei Li and Hosagrahar V Jagadish. 2014. Constructing an interactive natural language interface for relational databases. Proceedings of the VLDB Endowment, 8(1):73–84. [4]P. J. Price. 1990. Evaluation of spoken language systems: the ATIS domain. In Speech and Natural Language: Proceedings of a Workshop Held at Hidden Valley, Pennsylvania, June 24-27,1990. [5]Deborah A. Dahl, Madeleine Bates, Michael Brown, William Fisher, Kate Hunicke-Smith, David Pallett, Christine Pao, Alexander Rudnicky, and Elizabeth Shriberg. 1994. Expanding the scope of the ATIS task: The ATIS-3 corpus. In Human Language Technology: Proceedings of a Workshop held at Plainsboro, New Jersey, March 8-11, 1994. [6]Victor Zhong, Caiming Xiong, and Richard Socher. 2017. Seq2SQL: Generating structured queries from natural language using reinforcement learning. ArXiv preprint, abs/1709.00103. [7]Tao Yu, Rui Zhang, Kai Yang, Michihiro Yasunaga, Dongxu Wang, Zifan Li, James Ma, Irene Li, Qingning Yao, Shanelle Roman, Zilin Zhang, and Dragomir Radev. 2018c. Spider: A large- scale human-labeled dataset for complex and cross- domain semantic parsing and text-to-SQL task. In Proceedings of the 2018 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, pages 3911–3921, Brussels, Belgium. Association for Computational Linguistics. [8]Qingkai Min, Yuefeng Shi, and Yue Zhang. 2019a. A pilot study for Chinese SQL semantic parsing. In Proceedings of the 2019 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing and the 9th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (EMNLP-IJCNLP), pages 3652– 3658, Hong Kong, China. Association for Computational Linguistics. [9]Tao Yu, Rui Zhang, Michihiro Yasunaga, Yi Chern Tan, Xi Victoria Lin, Suyi Li, Heyang Er, Irene Li, Bo Pang, Tao Chen, Emily Ji, Shreya Dixit, David Proctor, Sungrok Shim, Jonathan Kraft, Vincent Zhang, Caiming Xiong, Richard Socher, and Dragomir Radev. 2019b. SParC: Cross-domain semantic parsing in context. In Proceedings of the 57th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, pages 4511–4523, Florence, Italy. Association for Computational Linguistics. [10]Victor Zhong, Mike Lewis, Sida I. Wang, and Luke Zettlemoyer. 2020b. Grounded adaptation for zero- shot executable semantic parsing. In Proceedings of the 2020 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), pages 6869– 6882, Online. Association for Computational Linguistics. [11]Bailin Wang, Wenpeng Yin, Xi Victoria Lin, and Caiming Xiong. 2021b. Learning to synthesize data for semantic parsing. In Proceedings of the 2021 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, pages 2760–2766, Online. Association for Computational Linguistics. [12]Ben Bogin, Jonathan Berant, and Matt Gardner. 2019a. Representing schema structure with graph neural networks for text-to-SQL parsing. In Proceedings of the 57th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, pages 4560–4565, Florence, Italy. Association for Computational Linguistics. [13]Bailin Wang, Richard Shin, Xiaodong Liu, Oleksandr Polozov, and Matthew Richardson. 2020a. RAT-SQL: Relation-aware schema encoding and linking for text-to-SQL parsers. In Proceedings of the 58th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, pages 7567–7578, Online. Association for Computational Linguistics. [14]Jiaqi Guo, Zecheng Zhan, Yan Gao, Yan Xiao, Jian-Guang Lou, Ting Liu, and Dongmei Zhang. 2019. Towards complex text-to-SQL in cross- domain database with intermediate representation. In Proceedings of the 57th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, pages 4524–4535, Florence, Italy. Association for Computational Linguistics. [15]Xiaojun Xu, Chang Liu, and Dawn Song. 2017. SQL-Net: Generating structured queries from natural language without reinforcement learning. preprint, abs/1711.04436. [16]Ansong Ni, Pengcheng Yin, and Graham Neubig. 2020. Merging weak and active supervision for semantic parsing. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, volume 34, pages 8536–8543. [17]John M Zelle and Raymond J Mooney. 1996. Learning to parse database queries using inductive logic programming. In Proceedings of the national conference on artificial intelligence, pages 1050–1055. [18]Catherine Finegan-Dollak, Jonathan K. Kummerfeld, Li Zhang, Karthik Ramanathan, Sesh Sadasivam, Rui Zhang, and Dragomir Radev. 2018. Improving text-to-SQL evaluation methodology. In Proceedings of the 56th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers), pages 351–360, Melbourne, Australia. Association for Computational Linguistics. [19]Ruiqi Zhong, Tao Yu, and Dan Klein. 2020a. Semantic evaluation for text-to-SQL with distilled test suites. In Proceedings of the 2020 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), pages 396–411, Online. Association for Computational Linguistics. [20]Peter Shaw, Ming-Wei Chang, Panupong Pasupat, and Kristina Toutanova. 2021. Compositional generalization and natural language variation: Can a semantic parsing approach handle both? In Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 11th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (Volume 1: Long Papers), pages 922–938, Online. Association for Computational Linguistics.

计算机术语审定委员会(Committee on Terminology)主要职能为收集、翻译、释义、审定和推荐计算机新词,并在CCF平台上宣传推广。这对厘清学科体系,开展科学研究,并将科学和知识在全社会广泛传播,都具有十分重要的意义。
术语众包平台CCFpedia的建设和持续优化,可以有效推进中国计算机术语的收集、审定、规范和传播工作,同时又能起到各领域规范化标准定制的推广作用。
新版的CCFpedia计算机术语平台(http://term.ccf.org.cn)将术语的编辑运营与浏览使用进行了整合,摒弃老版中跨平台操作的繁琐步骤,在界面可观性上进行了升级,让用户能够简单方便地查阅术语信息。同时,新版平台中引入知识图谱的方式对所有术语数据进行组织,通过图谱多层关联的形式升级了术语浏览的应用形态。
主任:
刘挺(哈尔滨工业大学)
副主任:
王昊奋(同济大学)
李国良(清华大学)
主任助理:
李一斌(上海海乂知信息科技有限公司)
执行委员:
丁军(上海海乂知信息科技有限公司)
林俊宇(中国科学院信息工程研究所)
兰艳艳(清华大学)
张伟男(哈尔滨工业大学)

 返回首页
返回首页